How to Make Windows Ignore an External HDD and Boot Faster
The more startup processes your PC has to go through, the longer it takes for your computer to boot up. One of these processes will check all attached hard drives to see which one contains the operating system. And if you’ve got a bunch of external hard drives plugged in that don’t have an operating system installed, they can slow things down indefinitely.
Here’s how to make Windows boot faster by ignoring external hard drives.
How can an external hard drive slow down Windows startup?
You may have one or more external hard drives connected to your computer. If you do this, the computer’s BIOS or UEFI may have to wait for both to boot before it knows where to boot from.
The more external drives you have connected, the longer this boot delay can be. The delay caused by this process shouldn’t be a problem if you’re using a fast and efficient computer. But on an older or less optimized PC, booting can take several seconds.
There are a few ways to get Windows to ignore your external hard drives at boot time. Some of these steps involve accessing the BIOS or UEFI menu, also known as the boot menu. It’s a good idea to make sure you’re familiar with them before proceeding.
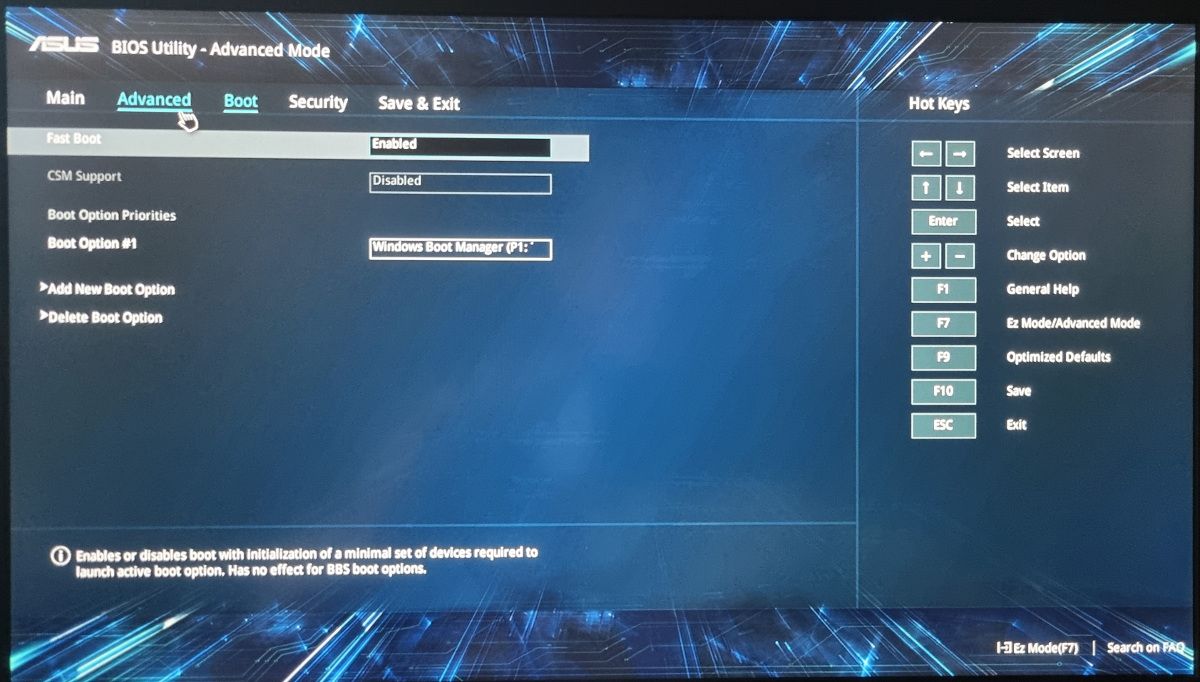
1. How to remove an external drive from the boot list
All external drives connected to your computer are automatically added to the boot list in BIOS or UEFI. Any disks that you want the system to ignore can usually be removed from this list.
You need to know how to access the start menu during startup to make this change. The exact process varies, but always involves pressing a function key when the computer starts up. The most commonly used keys are F2, F10 or F12.
- Reboot or restart your Windows PC and press the appropriate function key to enter the BIOS or EUFI boot menu.
- Find the boot options and look for the list that appears starting order.
- Select the drive you want to remove and look for the option to remove it from the boot list.
- Repeat for any other drives you want the boot process to ignore.
- Finally select Save changes and exit. The startup process will continue with the new settings and Windows will load.
Not all versions of BIOS or UEFI have the option to remove a volume from the boot list. In this situation, you should at least make sure that the drive containing Windows boots first. The devices at the top of the list are first in the boot order.
- To do this, select the drive containing the operating system in the boot list.
- The keys shown, typically the up/down arrow keys, are used to change the position of the drive.
- Make sure all external drives are at the bottom of the list. Or at least lower than the operating system drive.
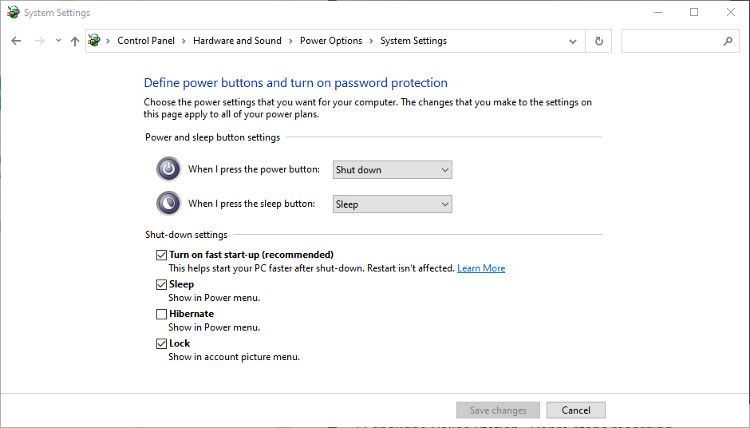
2. How to reset Fast Boot or Fast Startup
The Fast Boot or Fast Startup option is designed to make your Windows PC start faster. They may have been activated for a long time without giving you much thought. But when drives are repeatedly added and removed, their configurations can get messed up.
To reset Fast Boot or Fast Startup, all you have to do is disable, restart and re-enable the feature.
- Open Control Panel > System and Security > Power Optionsand click Choose what the power buttons do.
- Click the box next to Enable fast startup to disable it. If the option is grayed out, click Change settings that are currently unavailable. To do this, you must use an administrator account.
- Save the changes and shut down your PC. Don’t reboot; A complete shutdown is required here.
- Check that all your hard drives are connected, start your computer and re-enable Fast Boot/Fast Startup.
- Shut down again and ask Windows to create a new Fastboot file, then reboot.
If incorrect quick boot settings caused the slow boot time, you should notice a difference right away.
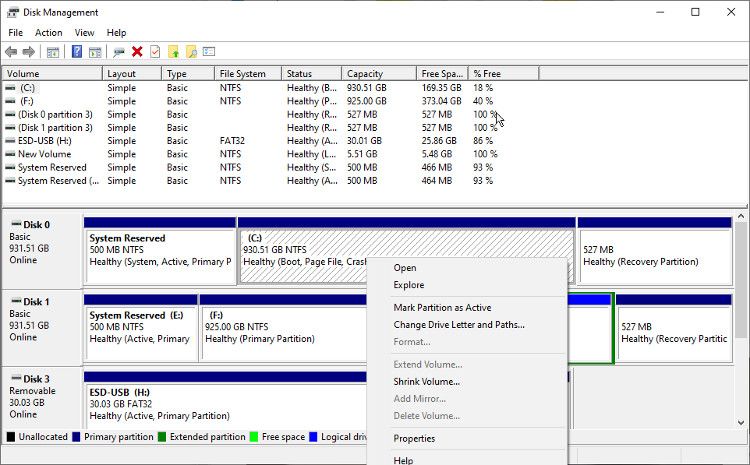
3. Set disk partitions as inactive
It’s really easy to learn how to partition a drive in Windows, but if your external hard drives have active partitions, the boot process will check if they are bootable volumes. This can also slow down the boot process.
You can easily set partitions to inactive using Windows Disk Management tool. Editing partitions can seem like a task best left to experts, but when editing a volume of storage, the risk of disaster is pretty low.
- Right click on the start menu press and select Disk Management from the power user menu.
- Locate the external hard drive at the bottom of the tool. The hard disks and partitions are displayed here.
- Right click on a partition and check if it is active or inactive as shown in the menu. If it is active, change it to inactive.
This does not affect how a storage volume works to copy files and data to it. You can still use them normally, they just won’t be checked during boot.
4. How to update your BIOS or UEFI
If the boot process is still slow, consider updating the BIOS or UEFI. The BIOS or UEFI installed on your computer probably has an updated version. Especially if your computer is more than 12 months old.
Updating the BIOS or UEFI is not the easiest task. But it shouldn’t be too much of a problem if you follow the update instructions carefully. You need to know your exact motherboard model and manufacturer. You can then check the manufacturer’s website for BIOS updates.
Make Windows ignore HDDs for faster boot times
Your connected external drives might make the boot time longer than necessary. Ensuring that the Windows boot process ignores drives that don’t need to be scanned can significantly improve boot time. This depends on how many hard drives you have connected, but when it comes to booting up the PC, faster is always better.