How to Compress Image Files on Linux Using Curtail
Storing and sharing large image files can be a headache. Fortunately, there are several ways to compress image files. If you work on Linux and prefer native tools, Curtail is a good image compression tool that you can use to compress images on your computer.
Let’s dive in to learn more.
What is truncation?
Curtail is a free, open-source image compression utility for Linux. It is based on GTK 3 and uses a number of open source projects to offer effective image compression. Curtail lets you compress PNG, JPEG, and WebP image files.
Curtail offers you the following functions:
- Easy to use GUI
- Compression of bulk images
- Lossless and lossy compression options
- Ability to set compression levels
- Option to preserve metadata and file attributes
- Support for JPEG, PNG and WebP image files
How to install Curtail on Linux
Curtail works on all major Linux distributions. Follow the instructions below to install it on your computer.
On Ubuntu and its derivatives, open the terminal and run the following commands to install Curtail:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apandada1/curtail
sudo apt update
sudo apt install curtailIf you are running another distribution on your computer, you can install Curtail via Flatpak. First, make sure Flatpak is installed on your computer. To do this, open the terminal and run this command:
flatpak If the above command returns a version number, you have Flatpak on your computer and you can proceed with the installation. Otherwise, install it first with our complete Flatpak guide.
Next, run this command to install Curtail:
flatpak install flathub com.github.huluti.CurtailAlternatively, if you don’t prefer either type of installation, you can build Curtail from source. To do this, first clone the curtail repository with:
git clone https:Then use the cd command to navigate to the curtail directory, like so:
cd CurtailFinally, enter these commands to build and install Curtail:
meson _build
cd _build
sudo ninja installHow to use Curtail to compress image files on Linux
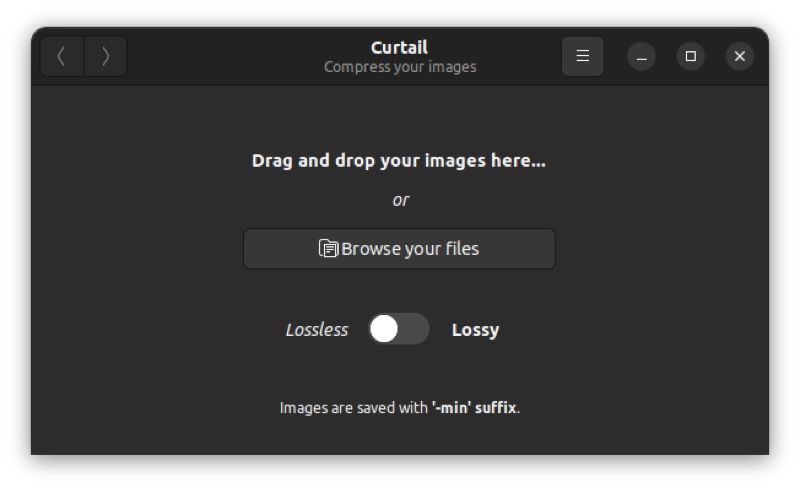
After installing Curtail on your computer, open the application menu, search for Curtail and launch it. A tiny window will pop up, and this is where all the magic happens.
Start by choosing a compression type between Lossless and lossy. For the uninitiated, lossy compression removes redundant bits of information from images, returning smaller image files, which are ideal for storage and sharing online.
On the other hand, lossless compression preserves pretty much all of the information in an image file, resulting in larger files. So according to your needs and the purpose of image compression, toggle the switch accordingly to select a compression type.
Next, Curtail will ask you to select the images you want to compress. There are two ways to do this. First, you can use the file manager to select the images. Or secondly, you can simply drag and drop image files onto Curtail.
If you want to use the file manager instead, click Browse your files and select the image files to compress. For the latter approach, open the file manager, select the images you want to compress – you can select multiple files at once – and drag them onto the crop window.
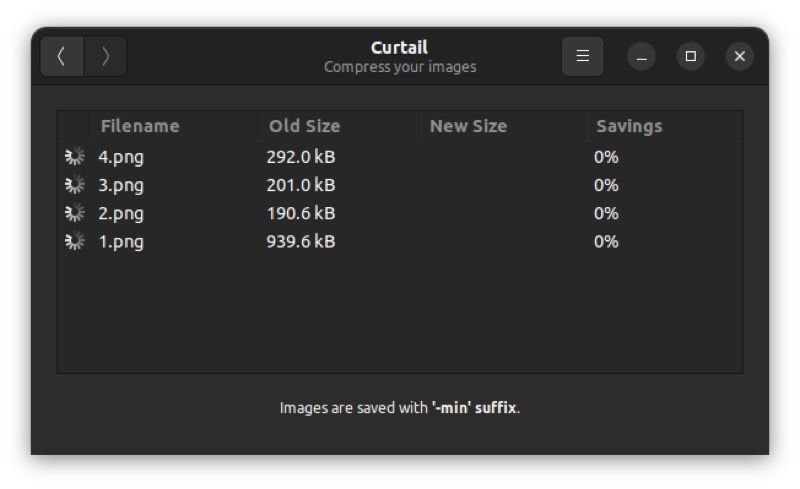
Shortly after you select image files, Curtail will start compressing them.
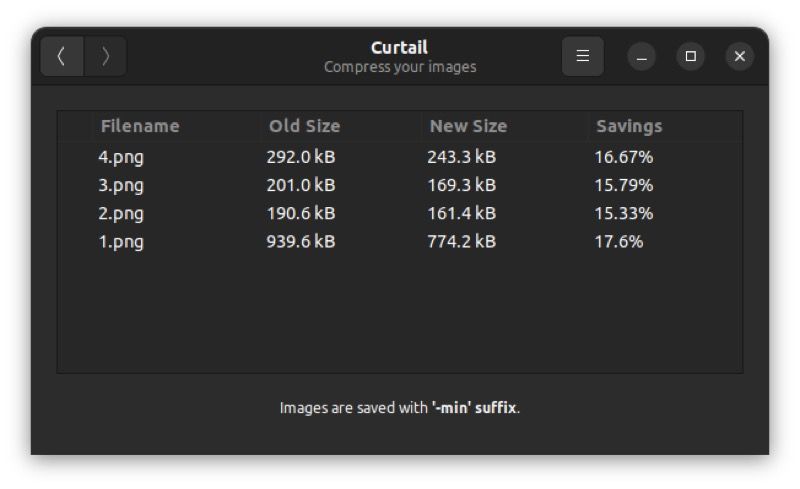
When the compression is complete, you’ll get a compression summary with details like the old file size, the new file size, and the savings you’ve made from the compression.
In addition, Curtail automatically saves the compressed images for you. You can find them in the same directory as their original counterparts. And to avoid confusion and to help you distinguish the original and compressed files, a “-min” suffix appears at the end of the compressed image files.
Adjust the curtail preferences to suit your needs
By default, Curtail works with predefined compression levels and uses specific settings. However, if you want to change the compression levels or tweak some of the settings to suit your needs, Curtail lets you do that.
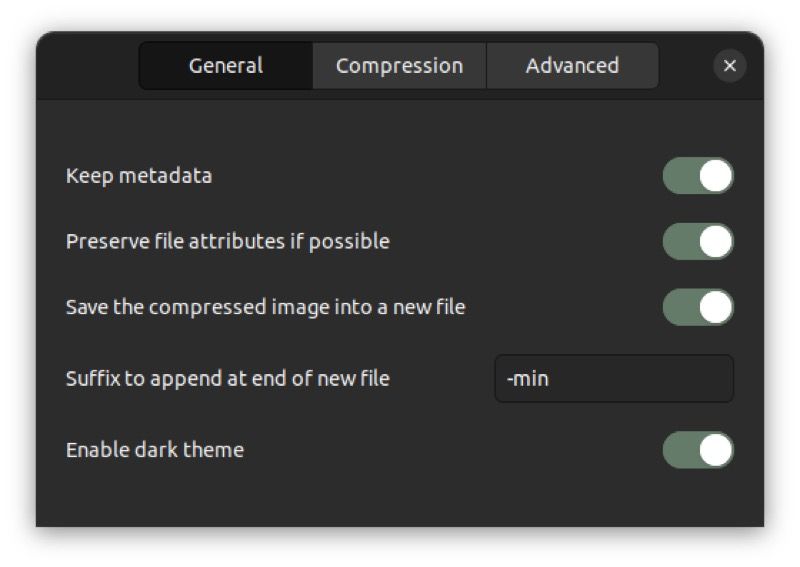
To change the curtail settings, click the hamburger menu in the main curtail window and select settings. Here you will see three tabs: General, compressionand Progressive, each containing a set of specific settings that you can change to your liking. Here are some options you might want to try:
1. Preserve metadata
If you want to preserve metadata from image files during compression, Curtail provides an option for that. In the Trim Settings window, go to General Tab and toggle the button for retain metadata when it is off.
2. Change the suffix for the new compressed files
Because Curtail saves compressed image files in the same directory as the original files, it adds the “-min” suffix to help you distinguish between the original and compressed images. However, if you don’t like this suffix and you want to use something else, you can.
Go to General Tab in the trimming settings. Click on the text box next to suffix and replace “min” with any text.
3. Replace the original image files
By default, Curtail saves compressed images as new files with a suffix at the end of their filename. However, if you don’t want this – and would rather replace the original images instead – turn that off Save the compressed image in a new file possibility from the General Tab in the trimming settings.
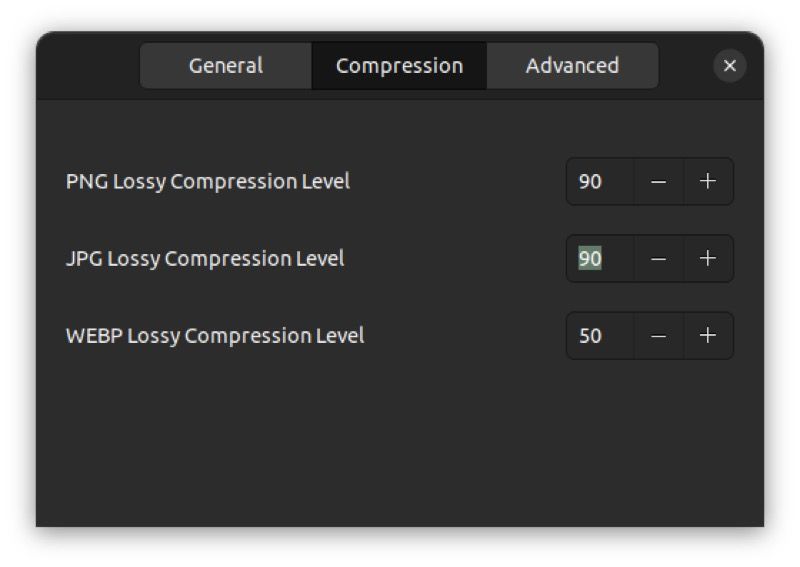
4. Change the lossy compression level
Curtail uses a fixed level of compression for different image formats. You can find these by opening the Curtail settings and going into that compression Tab. If you want to change the compression levels for any of these formats, press the minus (–) or plus (+) buttons next to the values accordingly.
5. Change the lossless compression level
Just like changing the lossy compression level, Curtail also allows you to change the lossless compression level. Go to the Progressive tab in the trimming settings and adjust the layers for PNG and WebP formats as you like.
Optimize image files for saving and sharing
While popular image editing tools like GIMP let you compress image files on Linux, the process is often complicated, making batch image compression a tedious task.
Curtail, on the other hand, greatly simplifies the compression process. It’s easy to use, works offline, and compresses image files in seconds to make them suitable for storage and sharing.
Alternatively, if you prefer web tools, you can compress image files online using many image compression tools available today.