What Does the Shell Infrastructure Host Process Do on Windows? How to Fix Its High Resources Consumption
Is the Shell Infrastructure Host process in Task Manager consuming a lot of your computer’s resources causing it to be slow and laggy? Is the resource consumption higher when opening a specific app or does it always remain the same?
In general, this process becomes resource-hungry when apps lose memory due to improper memory allocation, or when your personalization settings make graphics difficult to process.
In this article, we explain what the Shell Infrastructure Host process is doing and how to fix its high memory or other resource consumption.
What is the role of the shell infrastructure host process on Windows?
The Shell Infrastructure Host process, also known as sihost.exe, on Windows creates and maintains the graphical user interface for various Windows elements. Among other things, it handles the appearance of desktop backgrounds, pop-up notifications, and the taskbar. In that sense, it serves as a process that helps you navigate Windows and view Windows items.
In general, the Shell Infrastructure Host process consumes a small amount of CPU and RAM resources and doesn’t burden your system – just like any other Windows process. Occasionally, issues with certain apps or enabling certain Windows features can cause it to become resource hungry. That’s where the problem starts.
Has it also consumed a lot of resources on your computer? let’s fix it
How to reduce resource consumption by shell infrastructure host process
While some minor issues may arise, the Shell Infrastructure Host process consumes too many resources for two main reasons. Memory leaks in individual apps and incorrect personalization settings. In this way, you can reduce the burden on your resources of this process.
First, apply preliminary checks
Perform the following preliminary checks before proceeding with major fixes:
- Close all graphics-intensive apps and open them one at a time if you use several of them at the same time.
- Temporarily disable widgets and other desktop customizations.
- Go to Task Manager, locate Shell Infrastructure Host process, right click on it and press end task. After that, restart your computer. This gives the process a fresh start, which can help solve the problem.
- Make sure your Windows operating system is up to date.
- Make sure the Shell Infrastructure Host process is genuine and no virus scammer has named it.
- Run an SFC and DISM scan to repair corrupted system files that may be overloading your system. Our guide to the differences between CHKDSK, SFC, and DISM explains how to do each.
- Make sure your graphics drivers are up to date to ensure that outdated graphics drivers aren’t interfering with your display, which is causing the issue.
- Run a Microsoft Defender offline malware scan to rule out the possibility of viruses causing problems for the shell infrastructure host process.
If the above checks do not resolve the issue, you can reduce the resource consumption of the Shell Infrastructure Host process by checking for memory leaks in individual applications and tweaking personalization settings. How to rule out these two possibilities, we have explained below.
Rule out memory leak issues
A memory leak in graphics-intensive apps like the default Photos app, Paint 3D, and others is the first major reason why the Shell Infrastructure Host process is consuming too much memory. But what exactly is this memory leak?
A memory leak is nothing but the misallocation of memory resources. This means that some parts of your system memory become unusable even though they are free and not in use.
Therefore, when these apps take complete control of memory resources, fewer resources are available for other graphics processing, taxing the Shell Infrastructure Host process and causing it to consume excessive amounts of memory. Therefore, it is important to rule out the possibility of memory leaks first.
To do this, check if high resource consumption by the Shell Infrastructure Host process only occurs when you open a specific app, like the ones mentioned above. And if you close the app, will the resource consumption by the process go back to normal? If it does, then you have a memory leak problem.
To fix the memory leak problem with a specific app, just repair it. To do this, follow these steps:
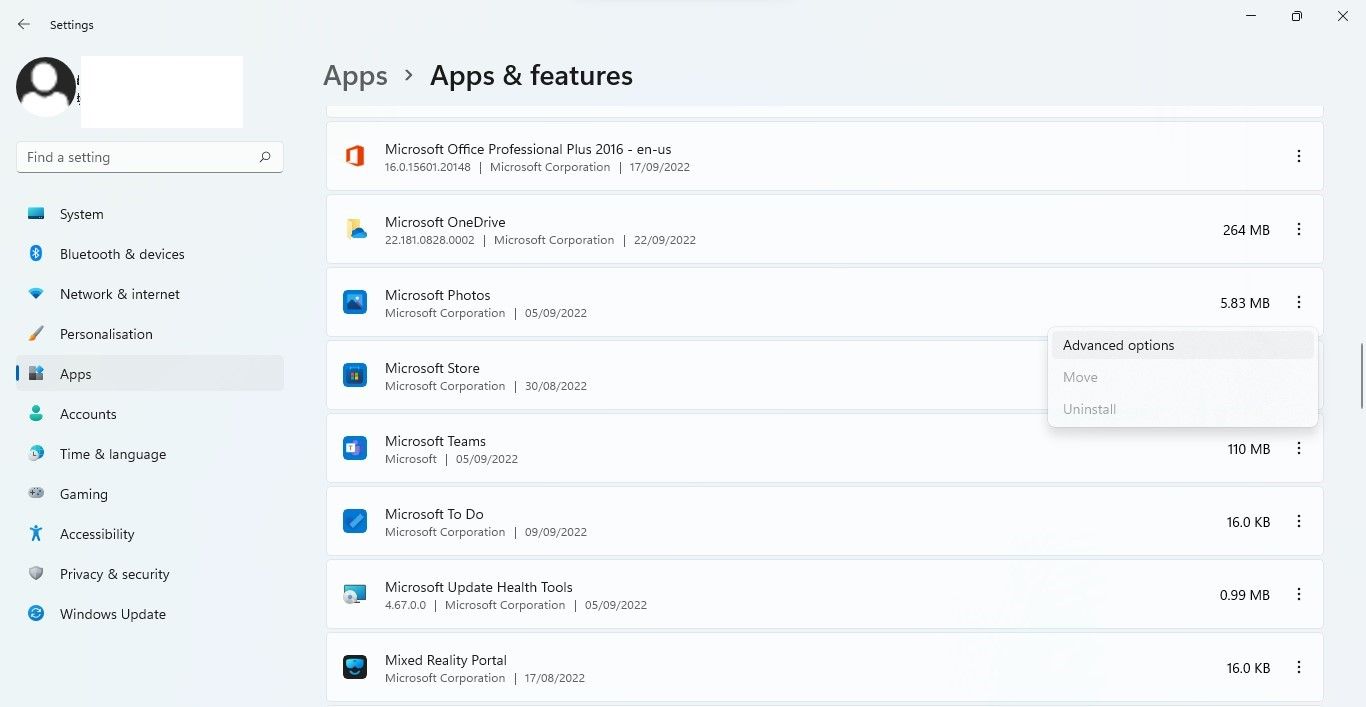
- Right click on the window beginning press and select applications and functions.
- Find the problematic app in the list.
- Click on that three vertical dots next to the app and select Expanded options.
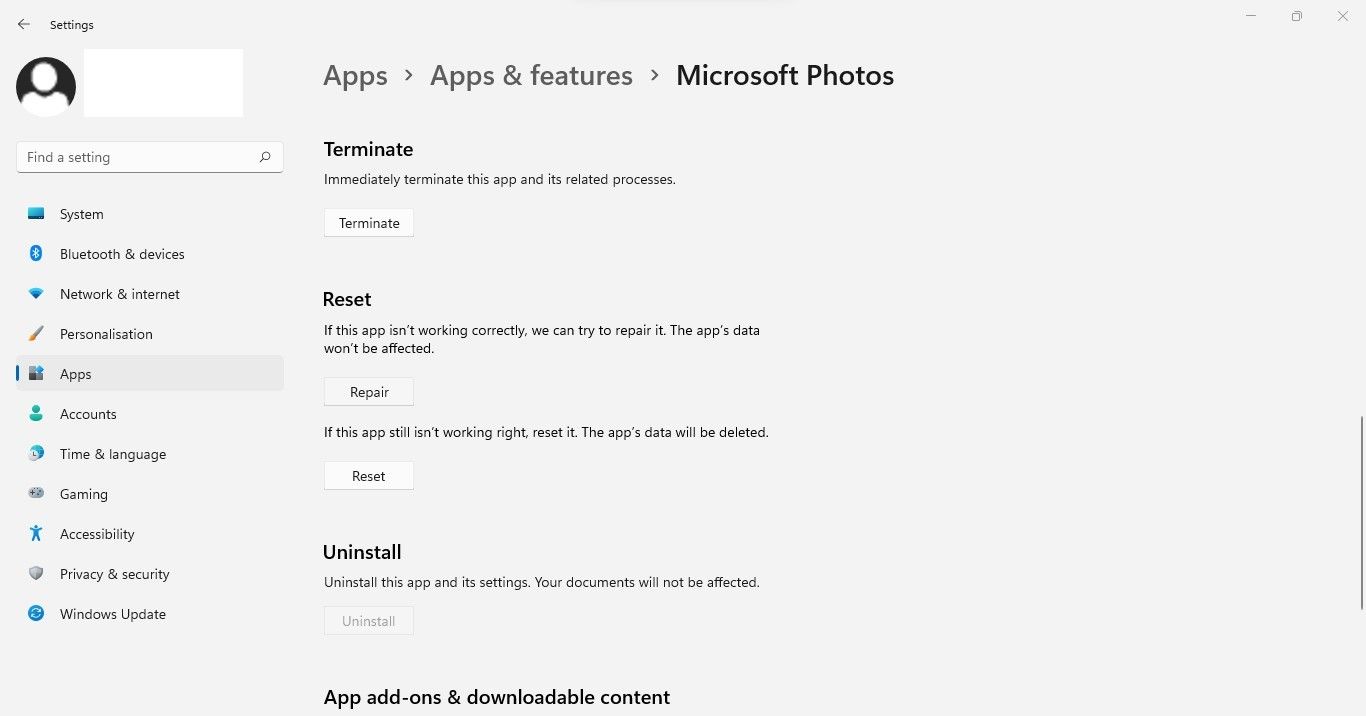
- Then scroll down and click repair.
You can also reset the app by clicking Reset to default button is directly below repair; if the repair does not solve the problem. If resetting the app doesn’t fix the problem, reinstall it.
If a clean install doesn’t fix the memory leak issue that’s still plaguing the Shell Infrastructure Host process, your best bet is to switch apps. Therefore, try an alternative app to the one you are encountering the problem with and you won’t have to worry about memory usage anymore.
What if the memory leak isn’t the problem and the Shell Infrastructure Host process is consuming all your resources even when no apps or programs are running? The following fix will help in such a situation.
Fine-tune your personalization settings
The Shell Infrastructure Host process handles most of the graphic elements in the Windows personalization settings, e.g. B. themes, colors, transparency effects, etc. By disabling or slightly tweaking some of these unnecessary features, you can reduce the workload of the Shell Infrastructure Host process.
Follow these steps to tweak personalization settings:
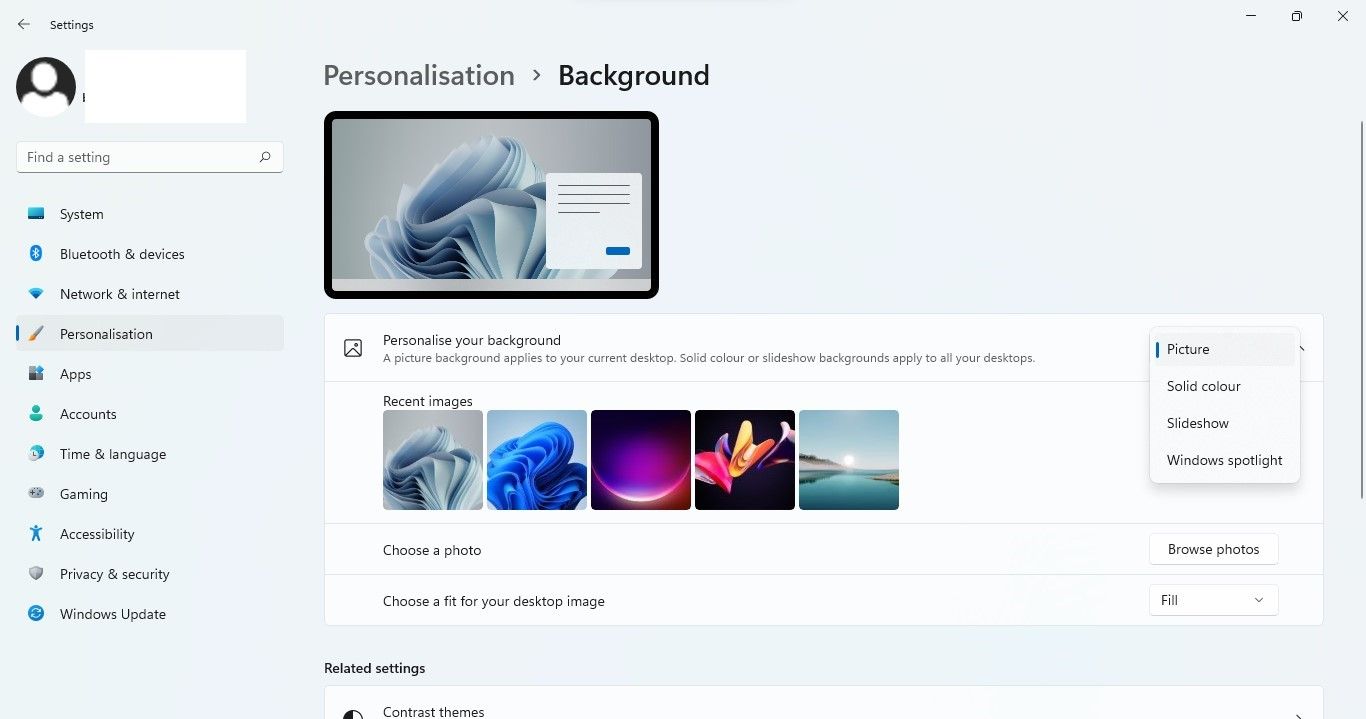
- When using the background slideshow or the Windows spotlight feature, you should first switch to a static background. To do this, right-click on Windows beginning press and select settings. Then click personalization in the left sidebar. After that, click on the drop-down menu next to Personalize your background and select picture. Finally, choose the wallpaper you want to use.
- If you have activated the contrast design function for better accessibility, press Left Alt + Left Shift and print screen to disable it.
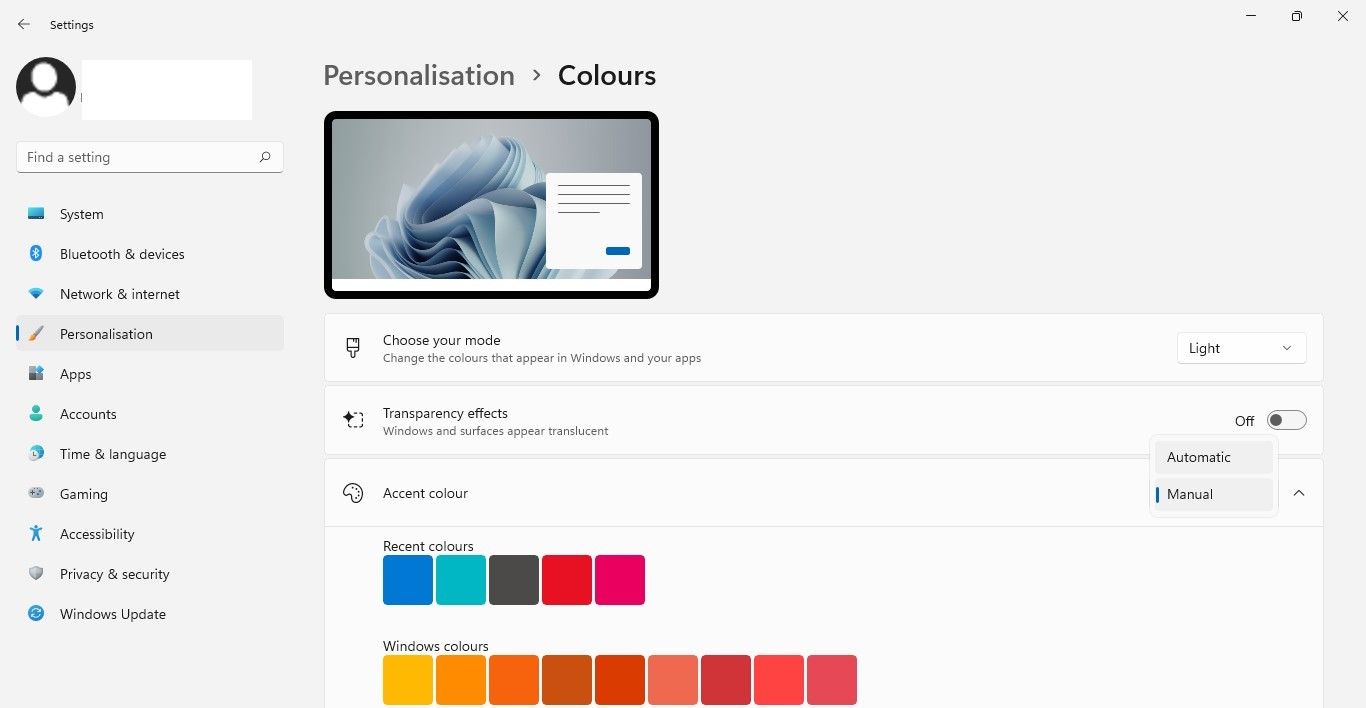
- Next, navigate to Personalization > Colors and turn off the switch next to transparency effects. Likewise if you use manual accent colorset it Automatically.
- Switch to a default Windows theme if you’re using a third-party graphics-intensive theme.
In the same way, you can disable or customize other features in the personalization settings that you think will not change the appearance. After making these changes, check again if it helped reduce the memory consumption by the Shell Infrastructure Host process. If not, move on to the next fix.
The last resort…
If none of the fixes helped you to solve the problem, you should disable background processes and services. Some of these processes continue to run in the background and burden the system’s resources without our knowledge. Make sure that’s not the case here.
Don’t let the shell infrastructure hosting process eat up your resources
Hopefully our article helped you better understand the Shell Infrastructure Host process. In addition, you can lower the resource consumption of the process when it consumes too much. If they fail, don’t disable this feature entirely, as it will do more harm than good.